You might think gaining mastery over charts and trends is the key to successful trading. But there is a secret weapon most traders often overlook – the economic calendar.
This tool gives you a sneak peek into the most important economic events and data releases that can move the market. In this post, we will get into the world of economic calendars, and show you how to use them.
What is an Economic Calendar?
An economic calendar is a list of upcoming economic events, data releases, and announcements that could impact financial markets. To be precise, it is like a roadmap to help you keep up with the constantly shifting economic scene. These calendars give traders a quick overview of the events, with time, date, and impact level, so they can prepare for market moves.
Key events on an economic calendar typically include:
- Economic Reports: Reports like GDP, unemployment rates, inflation, and manufacturing activity.
- Central Bank Decisions: Policy announcements and interest rate changes from institutions like the Fed or ECB.
- Geopolitical Events: Elections, summits, and regulatory changes that impact market sentiment.
- Confidence Indices: Surveys of consumer or business confidence that can be leading indicators of economic direction.
With its filterable interface, an economic calendar allows traders to focus on the events that really matter to them. This adaptability makes it a powerful tool for both short-term and long-term traders.
The Economic Calendar Features –What Does Its Layout Look Like?
Economic calendars are full of information that traders can use to prepare for market swings. Here is a breakdown of the calendar features and what they mean:
- Time: The exact time an event is scheduled to happen; generally adjusted for a trader’s local time zone.
- Currency: Displays the currency affected by the relevant event. For example, a U.S. GDP report primarily affects the USD.
- Impact Level: Represented by stars, colors, or other symbols to show the expected market impact of an event. For example:
- 1 star: Low impact
- 2 stars: Medium impact
- 3 stars: High impact
- Event Description: A brief description of the event, such as “Quarterly GDP Report” or “Consumer Price Index.”
- Actual, Forecast, and Previous Values:
- Actual: Indicates the actual reported data after the event.
- Forecast: Denotes analysts’ forecasts before the event.
- Previous: The previous reported data to compare.
Example:
If an economic calendar shows a US Initial Jobless Claims forecast of 220K and the actual is 232K, the difference could lead to a depreciation of the USD as higher unemployment means economic weakness.
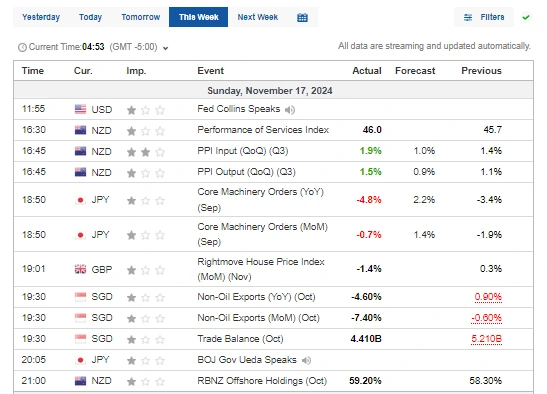
An example of economic calendar
Source: https://www.investing.com/economic-calendar/
How to Use an Economic Calendar
Let’s take a quick look at some easy steps for using an economic calendar:
Step 1: Set the Period
Select the period you want to focus on – today, this week, or next week. For short-term traders, daily updates might be enough. Whereas, the long-term traders might focus on updates spanning few weeks or months.
Step 2: Apply Filters
Filter the calendar by region, country, or currency. For example, a trader focused on EURUSD might want to monitor Eurozone and US events.
Step 3: Adjust Time Zones
Make sure event times are in your local time. This prevents confusion and helps with precise planning.
Step 4: Analyze Events
Click on each event to get more data, including historical trends, forecast values, and actual data. Understanding the history and context of an event helps you anticipate the market impact.
Step 5: Create Alerts
Set alerts for high-impact events that match your strategy. Alerts ensure that you never miss important updates.
Step 6: Build a Watchlist
Customize the calendar to focus on events that are relevant to your trading strategy, such as interest rate decisions, inflation reports, and employment data.
Why Traders Use Economic Calendars
Economic calendars are super useful for traders because they fill the gap between market guessing and actionable information.
Here is why traders use them:
- Market Awareness: By tracking key upcoming events, traders stay ahead of potential market movements.
- Risk Management: Anticipating volatility allows traders to prepare with strategies like stop-loss orders or reduced leverage.
- Faster Decision Making: Calendars present complex economic data in a simple way, saving traders hours of research.
- Strategy Adjustment: Traders can adjust their strategy as per the upcoming data releases or policy changes.
A Practical Use Case of Economic Calendar
Suppose that a forex trader is interested in trading the EURUSD currency pair. This trader can use an economic calendar to track the following:
- Upcoming ECB Decisions: European Central Bank interest rate announcements can have a huge impact on the Euro, so the trader sets alerts for these.
- U.S. Employment Data: He supplements his Watchlist with monthly non-farm payroll reports to measure the USD strength.
- Geopolitical Events: He monitors European elections and U.S. trade negotiations for gauging broader economic impacts.
By customizing the calendar and analyzing these events, he can make smarter decisions like taking long or short positions based on anticipated market trends.
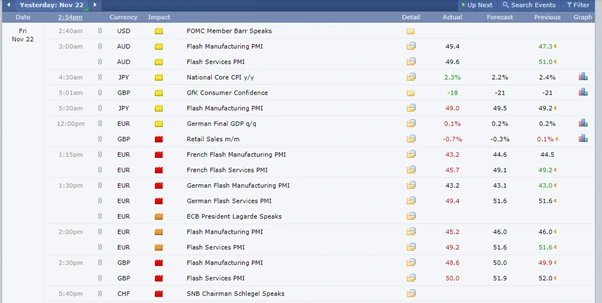
Source: https://www.forexfactory.com/
How to Trade with an Economic Calendar
Economic calendars are more than just dates and times, they are a trading tool to develop well-defined trading strategies. Here is how to trade with an economic calendar:
1. Trading the Market Moving Events
High-impact events like central bank decisions or GDP reports can significantly move the market. By knowing them in advance, traders can position themselves to trade the move.
Example: If the Fed is going to raise rates, traders might go long on USD assets, expecting a bullish move.
2. Prepare for Volatility
Some economic events cause big price movements. By using the calendar to anticipate volatility, traders can set stop-loss and take-profit levels.
Example: A forex trader expecting a big move on GBPUSD before a Bank of England announcement can set tight stop-loss to limit potential losses.
3. Combining Short Term and Long Term Analysis
Some events cause immediate price changes while others signal long-term economic trends. For a complete understanding, traders should look at both perspectives.
Example: A trader might use short-term data like monthly employment reports to confirm longer-term trends suggested by annual GDP growth.
4. Research Historical Patterns
Learn how past events have shaped markets to create predictive insights. This research-driven approach elevates trading outcomes.
Example: A trader might adjust his positions based on the observation that historically rising inflation data leads to depreciation of USD.
Common Mistakes to Avoid with Economic Calendars
Economic calendars are great tools but there are common pitfalls to watch out for:
- Overreacting: Do not act on every event – focus on those that are the most relevant to your strategy.
- Neglecting Context: Analyze economic data in the broader market environment.
- Ignoring Volatility: Underestimating the potential impact of high-importance events can lead to losses.
Conclusion
An economic calendar functions not only as a valuable tool but also as a strategic partner in navigating the fast-changing trading world. By customizing the calendar, looking at event details, and aligning insights with trading strategy, participants can get a notable edge in the markets.
Undoubtedly, trading becomes more effective when you leverage the power of an economic calendar to make smarter, more informed decisions.


